
The Climate Crisis Crossword
The climate Crisis—and our reporting on it—is ever-changing. See if you’re topped up on terminology from temperatures to transnational agreements.
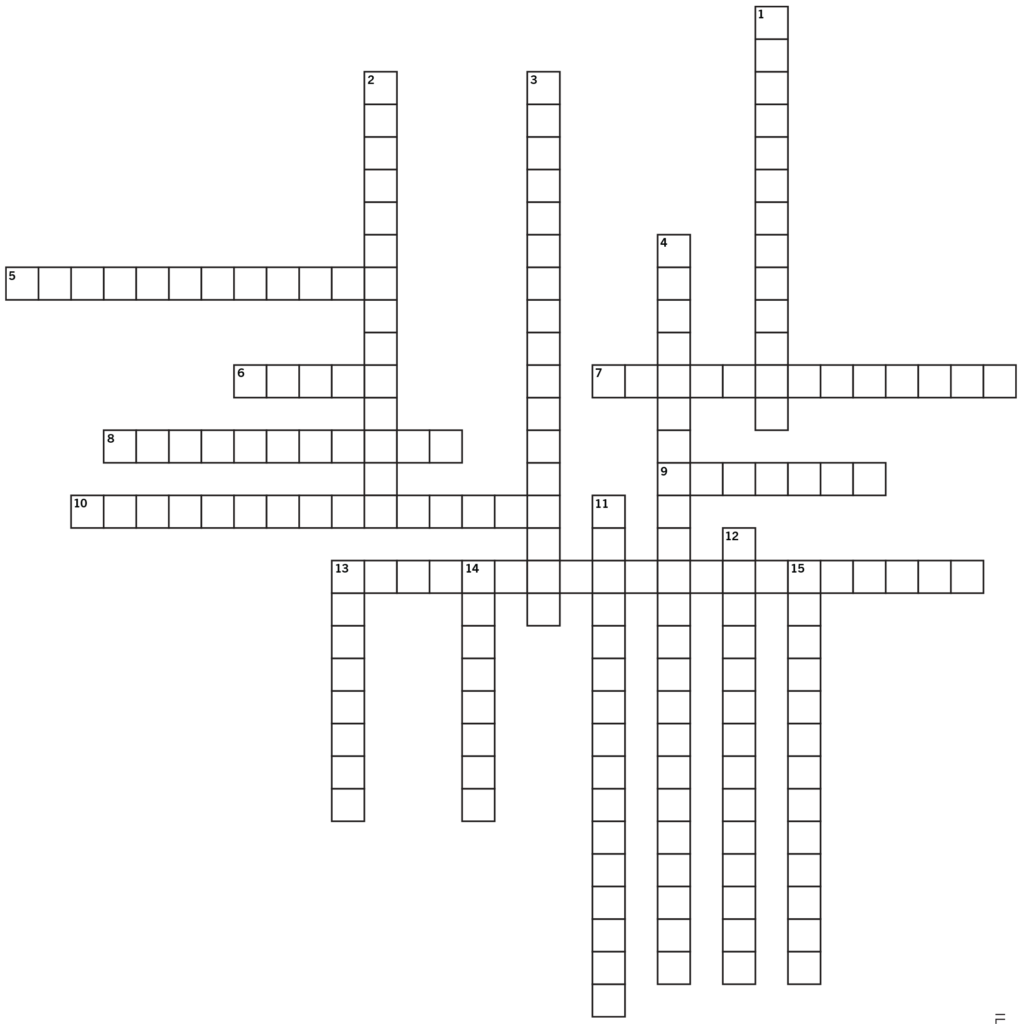
Down
1. A gradual increase in the earth’s overall temperature.
2. International treaty on climate change adopted by 196 parties.
3. Provides an unbiased and factual account of a particular topic.
4. Current affairs journalism related to nature and the environment.
11. The result of gases in the earth’s atmosphere.
12. Provides decision makers a framework of action to track and monitor the rate of climate change and ambitious action.
13. April 22 marks the anniversary of this modern environmental movement.
14. The activity that leads us to finding new facts and information.
15. A global foundation responsible for developing strategies and solutions essential to advancing international climate diplomacy and negotiation.
Across
5. The disinformation produced by an organization to present an environmentally responsible public image.
6. The depletion of this layer can cause increased amounts of UV radiation.
7. One carbon atom bonded to two oxygen atoms.
8. Formed over hundreds of millions of years by dead animals and plants that have died and broken down.
9. A colourless, odourless gas that occurs in nature and from certain human activities.
10. Total amount of greenhouse gases that are generated by human actions.
13. Looking at the climate crisis through a human-rights lens.
Answers
Down: 1. Global warming 2. Paris Agreement 3. Accurate reporting 4. Environmental journalism 11. Greenhouse effect 12. Climate reports 13. Earth Day 14. Research 15. United Nations
Across: 5. Greenwashing 6. Ozone 7. Carbon dioxide 8. Fossil fuels 9. Methane 10. Carbon footprint 13. Environmental justice
Climate Change: A Glossary
Accurate reporting: A document or presentation that provides factual and unbiased scientific data and information on a particular event, situation, or topic.
Air pollution: Contamination of the air that can harm the health of humans. Includes greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide or emissions from factories, cars, and planes.
Carbon footprint: The total amount of carbon emissions created by all the activities of a single person, group, or entity.
Carbon tax: The price imposed on emissions from fossil fuels.
Clean energy: Energy from renewable and zero-emission sources that do not pollute the atmosphere when used.
Climate reports: Key reports on climate impacts and solutions from the United Nations.
Environmental journalism: The presentation of unbiased scientific data and information relating to the environment, taking scientific information and making it accessible to nontechnical audiences. Environmental reporting aims to provide the basis for informed decision-making so individuals and policymakers can take positive action.
Environmental justice: A movement that works to ensure all people have the right to the same environmental protections and have adequate involvement in environmental policymaking.
Earth Day: Celebrated around the world on April 22 to demonstrate support for environmental protection.
Fossil fuels: A nonrenewable source of energy made from decomposing material of biological origin, usually from plant and animal matter. Over time, pressure and heat formed some of this matter into the materials we now know as coal, oil, and natural gas.
Global warming: The gradual increase of the earth’s overall temperature, occurring when carbon dioxide and other pollutants collect in the atmosphere.
Greenhouse effect: The process through which gases in the earth’s atmosphere trap heat, similar to the roof of a greenhouse. This produces what is known as greenhouse gases, which consist of carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons, and water vapour.
Greenwashing: False information produced by an organization to present an environmentally responsible public image. Claims may make the organization seem more environmentally responsible than they are.
Ozone layer: A layer of the earth’s atmosphere that absorbs the majority of ultraviolet light emitted by the sun.
Paris Agreement: A legally binding international climate-change treaty adopted by 196 parties in Paris in 2015. Its overall goal is to halt the increase of the earth’s global average temperature.
Renewable energy: Energy coming from a source that is naturally replenished, such as solar power, wind power, and hydroelectricity.
About the author

Mackenzie MacDonald
Mackenzie is a second-year Master of Journalism student at Toronto Metropolitan University. Passionate about solidarity journalism, her research interests include social justice and human rights issues, with a focus on gathering information and statistics, surrounding matters like gender equality, Indigenous rights, criminal justice and more.

